Introduction
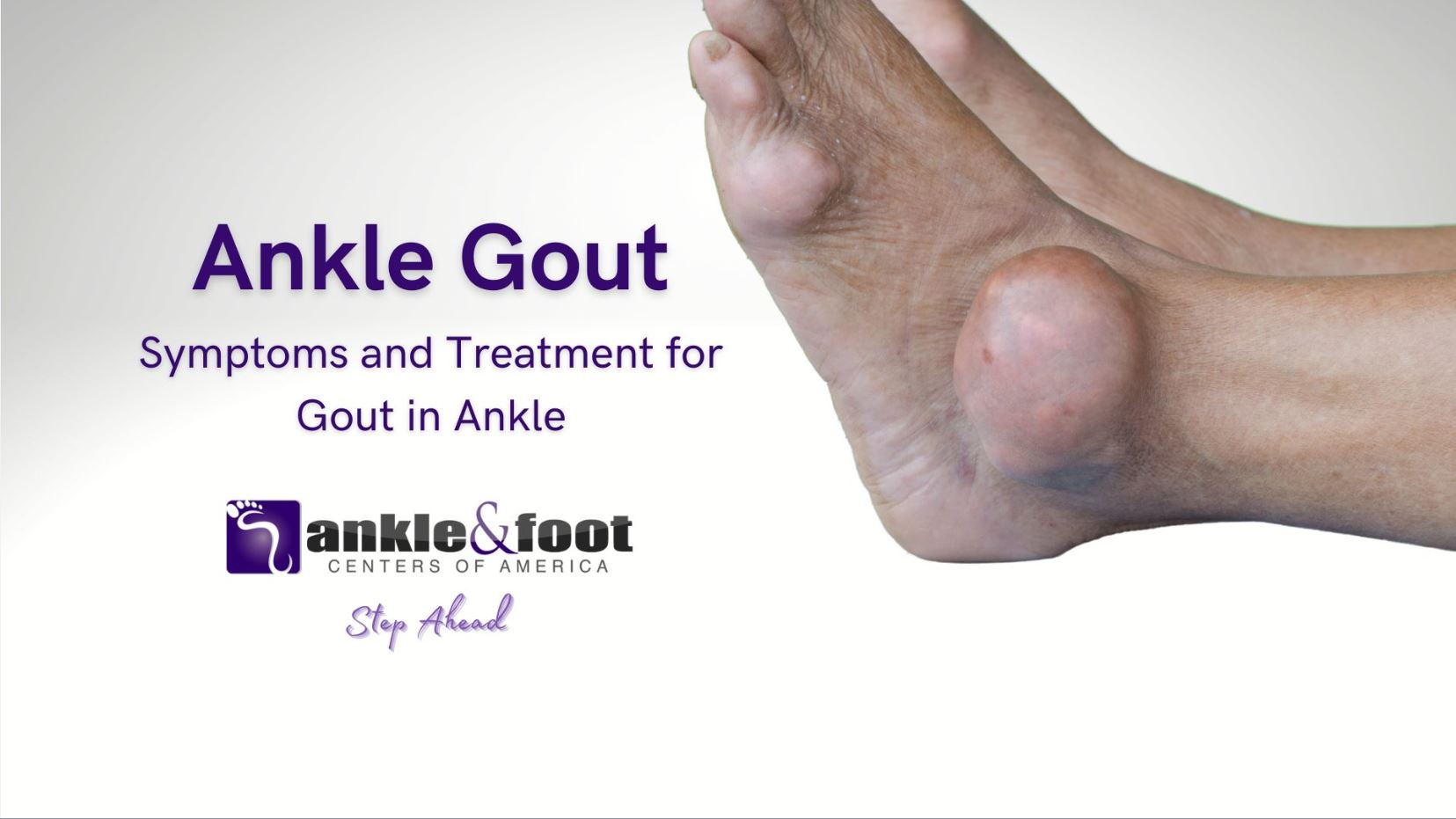
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, can have a significant impact on the lives of those affected. Among the various joints that gout can affect, the ankle joint is particularly susceptible. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and effective management strategies for ankle gout is crucial in providing relief and improving the quality of life for individuals experiencing this condition.
Gout is characterized by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe episodes of pain, inflammation, and swelling. When the ankle joint is affected, it can cause considerable discomfort and mobility limitations. Ankle gout attacks can occur unexpectedly, making it essential to be well-informed about the condition to effectively manage its symptoms.
In this article, we will delve into the details of ankle gout, exploring its symptoms, available treatment options, and strategies for effective management. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of ankle gout, individuals can better navigate their journey towards relief, minimize the impact of symptoms, and improve their overall well-being.
 Symptoms of Ankle Gout
Symptoms of Ankle Gout
Ankle gout presents with a distinct set of symptoms that can be debilitating during flare-ups. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective management. Here are the key indicators of ankle gout:
- Intense Joint Pain: Ankle gout is characterized by sudden and intense pain in the affected joint. The pain often strikes unexpectedly and can be excruciating, making it challenging to bear weight or move the ankle joint.
- Swelling and Inflammation: The affected ankle joint may become visibly swollen, red, and warm to the touch. This swelling is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals and the body’s inflammatory response to them.
- Tenderness and Sensitivity: Ankle gout can cause tenderness and sensitivity in the joint. Even the slightest touch or pressure can elicit pain and discomfort.
- Limited Range of Motion: During an ankle gout attack, the range of motion in the joint may be significantly reduced. Flexing, extending, or rotating the ankle can be challenging and painful.
- Skin Changes: In some cases, the skin over the affected ankle joint may appear shiny and stretched. It may also feel tight and exhibit a purplish or reddish discoloration.
It’s important to note that ankle gout symptoms can vary in severity and duration. Some individuals may experience infrequent flare-ups, while others may have recurrent or chronic symptoms. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis and Risk Factors
Diagnosing ankle gout involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history assessment, and diagnostic tests. A healthcare professional, such as a rheumatologist, will typically perform the following steps to confirm a diagnosis:
- Medical History Evaluation: The healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, their duration, and any previous occurrences. They will also assess your medical history, including family history of gout or other related conditions.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination will be conducted to assess the affected ankle joint for signs of inflammation, tenderness, swelling, and limited range of motion. The examination helps rule out other possible causes of ankle pain.
- Joint Aspiration: To definitively diagnose ankle gout, a joint aspiration or arthrocentesis may be performed. During this procedure, a small needle is inserted into the ankle joint to withdraw a sample of synovial fluid. The fluid is then examined under a microscope to check for the presence of uric acid crystals.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to measure the levels of uric acid in your blood. Elevated uric acid levels, although not conclusive on their own, can support the diagnosis of gout. However, it’s important to note that some individuals with gout may have normal uric acid levels during an acute attack.
Once diagnosed with ankle gout, understanding the risk factors associated with its development is crucial for effective management. Some common risk factors include:
- High Uric Acid Levels: Elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, known as hyperuricemia, increase the risk of developing gout. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, which are found in certain foods and are also produced by the body.
- Dietary Choices: Consumption of purine-rich foods, such as organ meats, seafood, red meat, and sugary beverages, can contribute to increased uric acid levels and gout risk. Alcohol, especially beer, has also been associated with higher gout risk.
- Obesity and Weight Gain: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing gout. Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, potentially leading to the accumulation of uric acid crystals.
- Family History: Gout can have a genetic component, and individuals with a family history of gout are more likely to develop the condition.
- Age and Gender: Gout is more common in men, particularly after the age of 40. Women are at a higher risk after menopause, when their uric acid levels may rise.
By understanding the diagnosis process and recognizing the risk factors associated with ankle gout, individuals can work with their healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan and make lifestyle modifications to effectively manage the condition.
Treatment Options for Ankle Gout
 Ankle gout treatment in Nashville aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, prevent future flare-ups, and manage the underlying causes. The treatment plan may involve a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and self-care strategies. Here are the main treatment options for ankle gout:
Ankle gout treatment in Nashville aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, prevent future flare-ups, and manage the underlying causes. The treatment plan may involve a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and self-care strategies. Here are the main treatment options for ankle gout:
- Medication:
• Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation during gout attacks.
• Colchicine: This medication can be prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation. It is often used in the early stages of an attack.
• Corticosteroids: In severe cases or when NSAIDs and colchicine are not suitable, corticosteroids may be injected directly into the ankle joint to reduce inflammation and provide relief. - Lifestyle Changes:
• Dietary Modifications: Limiting the intake of purine-rich foods, alcohol, and sugary beverages can help manage uric acid levels and reduce the frequency of gout attacks.
• Hydration: Staying well-hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water can assist in flushing out excess uric acid.
• Weight Management: Losing weight, if necessary, can help decrease the risk of gout attacks, as it reduces the strain on the joints.
• Exercise: Engaging in regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can strengthen the joints, improve mobility, and reduce the risk of gout flare-ups. - Self-Care Strategies:
• Applying Ice Packs: During an acute gout attack, applying ice packs to the affected ankle can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
• Resting and Elevating: Resting the affected ankle and elevating it on a cushion or pillow can assist in reducing swelling and promoting healing.
• Protecting the Joint: Wearing comfortable, supportive footwear and using assistive devices, such as crutches or a cane, can help protect the ankle joint and prevent further damage.
It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on the severity and frequency of ankle gout attacks. Regular follow-up visits are crucial to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments.
Managing Ankle Gout: Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatment, incorporating certain lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to managing ankle gout and reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Dietary Modifications:
• Limit Purine-Rich Foods: Reduce the consumption of purine-rich foods such as organ meats, shellfish, red meat, and certain types of seafood. These foods contribute to elevated uric acid levels in the body.
• Increase Low-Fat Dairy Intake: Low-fat dairy products, such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, have been associated with a lower risk of gout. They may help to lower uric acid levels.
• Stay Hydrated: Drinking an ample amount of water throughout the day can help dilute uric acid and promote its excretion from the body. - Weight Management:
• Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight can reduce the strain on the joints, including the ankles. Aim for gradual weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise. - Exercise and Physical Activity:
• Low-Impact Exercises: Engage in low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling. These exercises can help improve joint function, strengthen the muscles supporting the ankle joint, and promote overall joint health.
• Range-of-Motion Exercises: Perform gentle range-of-motion exercises for the ankle joint to enhance flexibility and prevent stiffness.
• Avoid High-Impact Activities: Minimize or avoid high-impact activities that put excessive stress on the ankles, such as running or jumping. - Stress Reduction:
• Manage Stress Levels: High levels of stress can potentially trigger gout attacks. Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies to help reduce stress. - Avoid Triggering Factors:
• Limit Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol, especially beer, is known to increase uric acid levels and raise the risk of gout attacks. Limit alcohol intake or avoid it altogether.
• Be Mindful of Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics or certain types of chemotherapy drugs, can raise uric acid levels. Consult with your healthcare provider about the potential impact of medications on gout.
By adopting these lifestyle changes, individuals with ankle gout can actively manage their condition and reduce the frequency and intensity of flare-ups. It is important to note that lifestyle modifications should be personalized to each individual’s specific needs and medical advice.
Natural Remedies for Ankle Gout
In addition to medical treatment and lifestyle modifications, some individuals with ankle gout may find relief through natural remedies. It’s important to note that these remedies should be used as complementary approaches and discussed with a healthcare professional. Here are some natural remedies that may provide support:
- Cherry Juice: Cherry juice, particularly tart cherry juice, has been associated with reducing the frequency of gout attacks. It contains compounds that may help lower uric acid levels and have anti-inflammatory properties. Consider incorporating cherry juice into your diet, but be mindful of its sugar content.
- Turmeric: Turmeric, a spice widely known for its anti-inflammatory properties, may offer benefits for individuals with ankle gout. It contains an active compound called curcumin, which has been studied for its potential to reduce inflammation. Consider adding turmeric to your meals or consuming it as a supplement, following appropriate dosage guidelines.
- Ginger: Ginger has been used for centuries for its anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with ankle gout. Incorporate ginger into your diet by adding it to meals, drinking ginger tea, or using ginger supplements with guidance from a healthcare professional.
- Bromelain: Bromelain is an enzyme found in pineapple that has anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce pain and inflammation associated with gout. Consult with a healthcare professional about bromelain supplements and appropriate dosage.
- Epsom Salt Soaks: Soaking the affected ankle in warm water with Epsom salt can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation. Epsom salt contains magnesium, which may help relax muscles and reduce discomfort.
It’s important to remember that natural remedies may vary in their effectiveness for individuals, and what works for one person may not work for another. Additionally, natural remedies should not replace medical treatment or lifestyle modifications but should be used as complementary strategies.
Prevention of Ankle Gout
While managing ankle gout through treatment and lifestyle changes is crucial, taking preventive measures is equally important to minimize the frequency of gout attacks and maintain overall joint health. Here are some strategies to consider for preventing ankle gout:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet:
• Choose Low-Purine Foods: Opt for a balanced diet that includes low-purine foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
• Moderate Purine-Rich Foods: If you choose to consume purine-rich foods, do so in moderation and balance them with low-purine options.
• Limit Alcohol Intake: Reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption, especially beer, as it can significantly increase the risk of gout attacks. - Stay Hydrated:
• Drink Ample Water: Proper hydration helps in diluting uric acid and promoting its excretion from the body. Aim for at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water per day. - Maintain a Healthy Weight:
• Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Losing excess weight can help reduce the strain on the joints, including the ankles. Follow a well-balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity to achieve a healthy weight. - Avoid Triggers:
• Identify Personal Triggers: Pay attention to factors that may trigger gout attacks in your specific case, such as certain foods, alcohol, or stressful situations. Minimize or avoid these triggers as much as possible. - Regular Medical Check-ups:
• Consult with a Healthcare Professional: Regularly visit your healthcare provider to monitor your condition, assess uric acid levels, and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
• Discuss Medications: Inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking, as some medications can increase the risk of gout. They may recommend alternatives if necessary.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals with ankle gout can actively reduce the occurrence of gout attacks and maintain better control over their condition. However, it is important to remember that gout is a complex condition influenced by various factors, and individual experiences may vary.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
When left untreated or poorly managed, ankle gout can lead to several complications and have long-term effects on joint health and overall well-being. It is essential to be aware of these potential consequences and prioritize ongoing care and monitoring. Here are some aspects to consider:
- Joint Damage: Recurrent ankle gout attacks can cause damage to the joint structures over time. The accumulation of uric acid crystals can lead to the formation of tophi, which are hard deposits that can cause joint deformities and impair joint function.
- Chronic Pain and Disability: Ankle gout that is not effectively managed can result in chronic pain, joint stiffness, and limited mobility. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities, diminish quality of life, and lead to disability.
- Kidney Stones: In some cases, individuals with gout may also develop kidney stones. Uric acid crystals can form in the kidneys, leading to the formation of stones that can cause pain, urinary tract infections, and kidney damage.
- Impact on Overall Health: Gout has been associated with an increased risk of other health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, and metabolic syndrome. Proper management of ankle gout is crucial to minimize these risks and maintain overall health.
To prevent complications and manage ankle gout effectively, it is important to prioritize ongoing care and monitoring:
- Regular Follow-up Visits: Continue to visit your healthcare provider as scheduled to assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan, monitor uric acid levels, and make any necessary adjustments.
- Open Communication: Maintain open and honest communication with your healthcare provider. Discuss any changes in symptoms, medication side effects, or concerns you may have regarding your ankle gout.
- Self-Monitoring: Stay attentive to your body and learn to recognize early signs of gout attacks. By being proactive, you can take timely action to manage symptoms and prevent severe flare-ups.
- Lifestyle Maintenance: Continue to follow the recommended lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, weight management, regular exercise, and staying hydrated. These habits are crucial for long-term management of ankle gout.
By prioritizing ongoing care, individuals with ankle gout can minimize the risk of complications, improve joint health, and enhance their overall quality of life.
Summary and Conclusion
 Gout in the Ankle, characterized by intense joint pain, swelling, and inflammation, can significantly impact the lives of those affected. Understanding the symptoms, seeking timely diagnosis, and implementing appropriate treatment and management strategies are crucial for individuals with ankle gout.
Gout in the Ankle, characterized by intense joint pain, swelling, and inflammation, can significantly impact the lives of those affected. Understanding the symptoms, seeking timely diagnosis, and implementing appropriate treatment and management strategies are crucial for individuals with ankle gout.
In this article, we explored the symptoms of ankle gout, the diagnosis process, and the risk factors associated with its development. We discussed various treatment options, including medication and lifestyle changes, emphasizing the importance of personalized approaches. Furthermore, we explored lifestyle modifications, natural remedies, and preventive measures that can complement medical treatment in managing ankle gout effectively.
We highlighted the significance of ongoing care, regular check-ups, and self-monitoring to prevent complications and ensure long-term management. Complications such as joint damage, chronic pain, and the formation of kidney stones were addressed, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive care.
It is essential for individuals with ankle gout to work closely with healthcare professionals, follow recommended treatment plans, and make necessary lifestyle modifications. By adopting a proactive approach, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks, manage symptoms, and improve their overall quality of life.
Remember, ankle gout is a complex condition influenced by various factors, and experiences may differ among individuals. By staying informed, seeking appropriate care, and making informed decisions, individuals can successfully navigate their journey with ankle gout.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding ankle gout management.